Brain Hemorrhage Causes, Symptoms & Emergency Action
The brain hemorrhage causes is a serious and life-threatening medical emergency that requires immediate attention. It happens when a blood vessel inside the brain ruptures and causes bleeding in the brain. This bleeding puts pressure on brain tissue, reduces oxygen supply, and can damage vital brain functions.
Understanding the causes, symptoms, types, and treatment options of brain hemorrhage helps people act quickly during emergencies.

What Is Brain Hemorrhage?
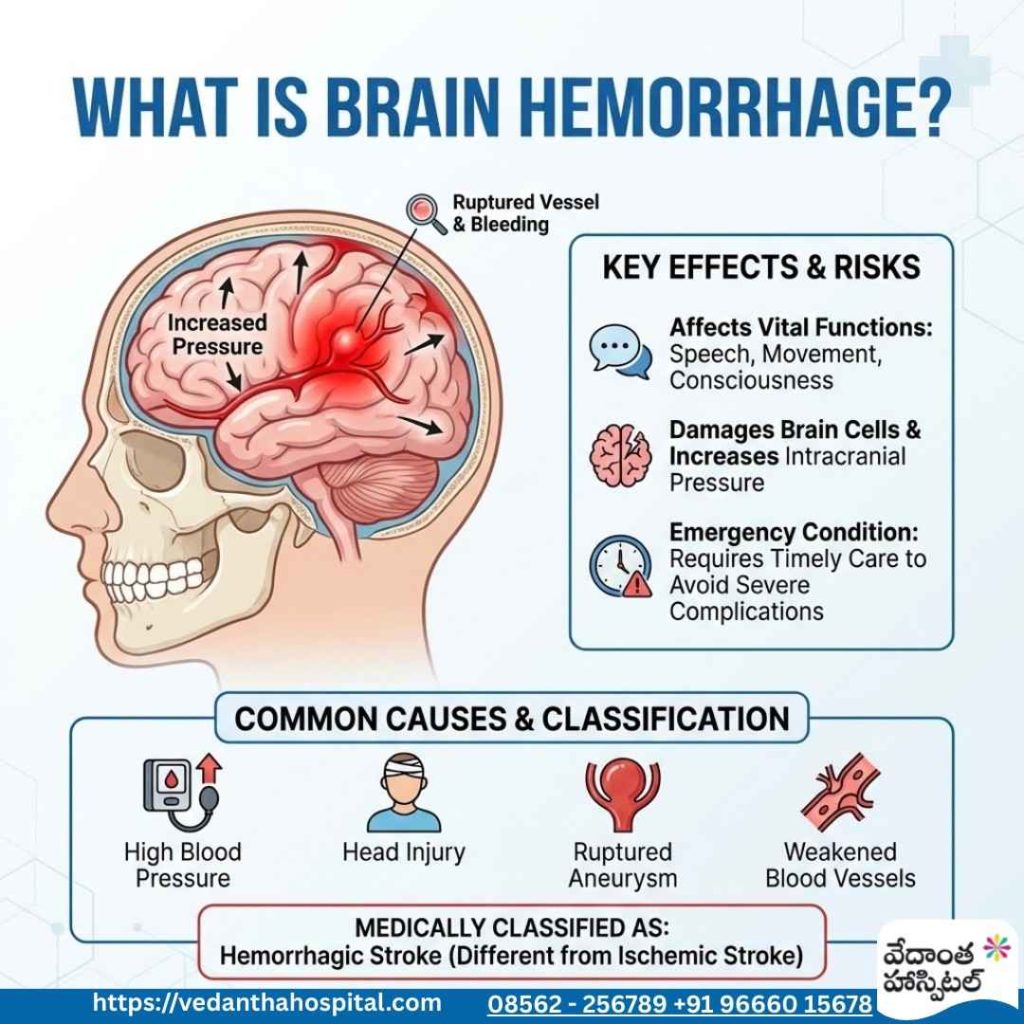
The brain hemorrhage is an serious medical condition where a blood vessel inside the brain ruptures and causes bleeding in the brain. This bleeding damages nearby brain cells and increases pressure inside the skull, which can quickly affect vital brain functions such as speech, movement, and consciousness. Because the brain is enclosed in a hard skull, even a small amount of bleeding can lead to severe complications.
Medically, hemorrhage is classified as a hemorrhagic stroke, which differs from an ischemic stroke caused by a blocked blood vessel. In hemorrhage cases, the sudden release of blood reduces oxygen supply to brain tissue and leads to brain swelling, making emergency treatment critical. Without timely care, the condition can worsen rapidly.
A brain hemorrhage can occur due to high blood pressure, head injury, ruptured aneurysm, or weakened blood vessels. The severity depends on the size, location, and speed of bleeding. Early diagnosis using a CT scan brain or MRI brain, followed by immediate medical or surgical care, greatly improves survival and recovery chances.
Types of Brain Bleeding
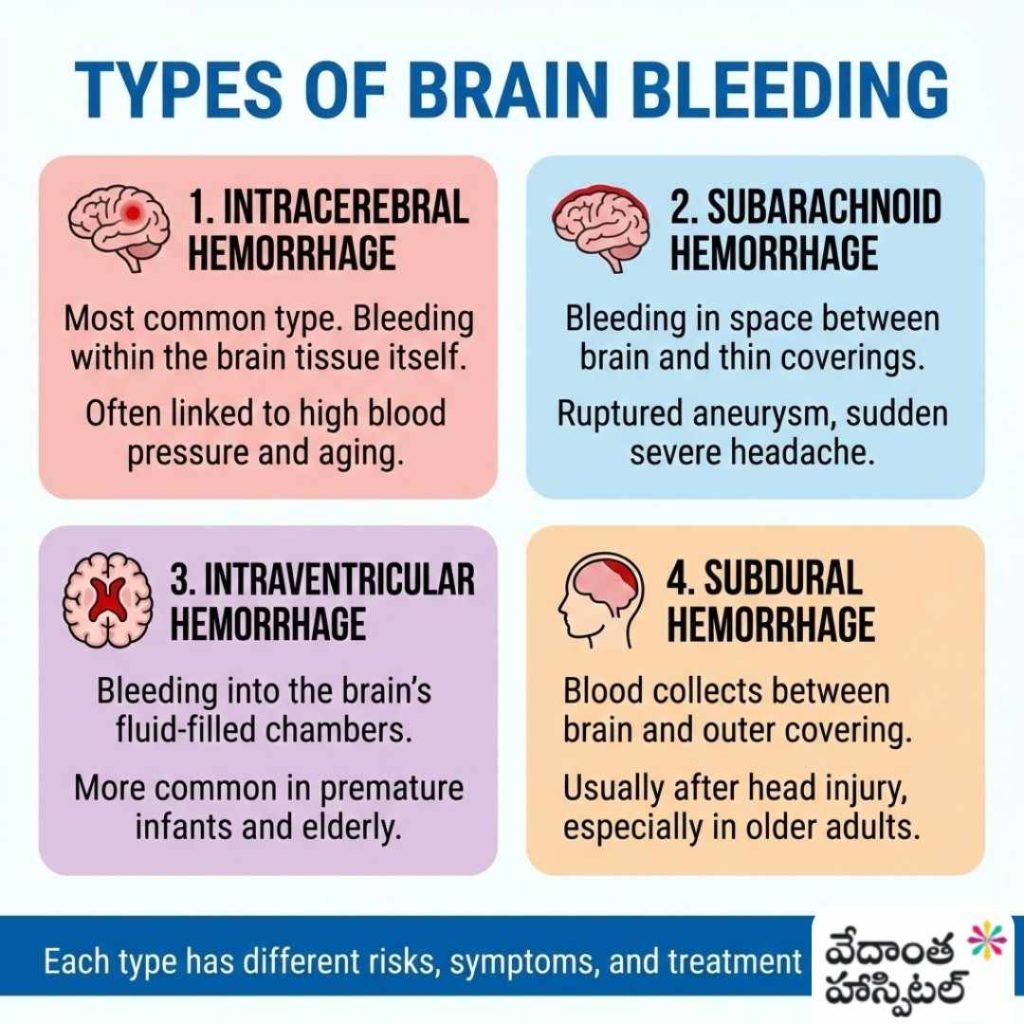
There are different types of brain hemorrhage, depending on where the bleeding occurs:
1. Intracerebral Hemorrhage
This is the most common type and happens within the brain tissue itself. Intracerebral hemorrhage is often linked to high blood pressure and aging.
2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
Subarachnoid hemorrhage occurs in the space between the brain and the thin tissues covering it. It is frequently caused by a ruptured aneurysm and presents with a sudden, severe headache.
3. Intraventricular Hemorrhage
Bleeding occurs into the brain’s fluid-filled chambers and is more common in premature infants and elderly patients.
4. Subdural Hemorrhage
Blood collects between the brain and its outer covering, usually after head injury, especially in older adults.
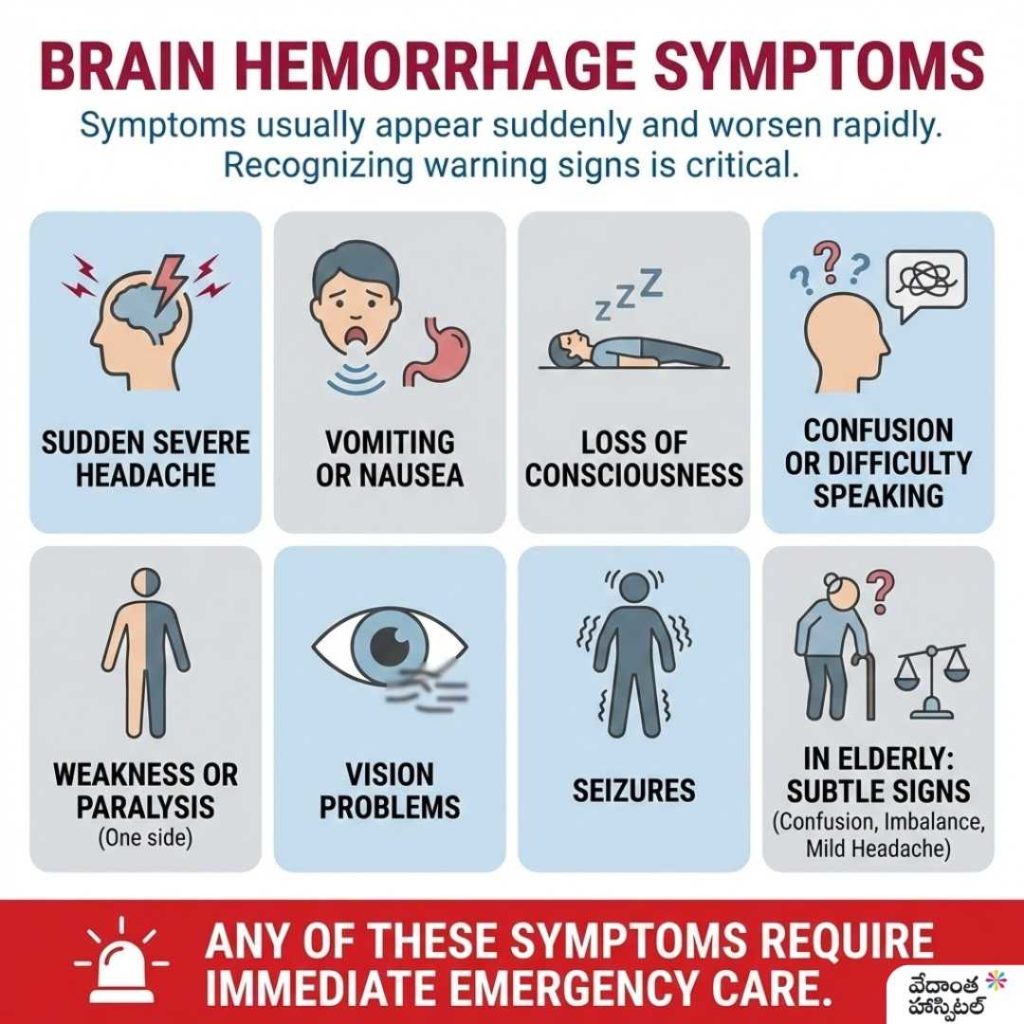
Brain hemorrhage symptoms
Brain Hemorrhage symptoms usually appear suddenly and worsen rapidly. Recognizing these warning signs is critical.
Common symptoms include:
- Sudden severe headache
- Vomiting or nausea
- Loss of consciousness
- Confusion or difficulty speaking
- Weakness or paralysis on one side of the body
- Vision problems
- Seizures
In elderly individuals, brain hemorrhage causes in old age symptoms may be subtle at first, such as confusion, imbalance, or mild headache, which can delay diagnosis.
Any of these symptoms require immediate emergency care.
Brain Hemorrhage Causes
Understanding brain hemorrhage causes that helps to reduce risk and supports early prevention.
Major causes include:
- Uncontrolled high blood pressure
- Head injury or trauma
- Ruptured aneurysm (ruptured blood vessel in brain)
- Blood-thinning medications
- Abnormal blood vessels
- Brain tumors
- Liver disease affecting blood clotting
Conditions related to intracerebral bleeding causes are more common in people with chronic hypertension or lifestyle-related risks.
Brain Hemorrhage Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the type, size, and location of bleeding, as well as the patient’s overall condition. Emergency treatment focuses on saving life and preventing further brain damage.
Treatment Type | Purpose | When It Is Used |
Emergency Stabilization | Control blood pressure, breathing, oxygen | Immediately after diagnosis |
CT Scan Brain / MRI Brain | Confirm bleeding location and size | During diagnosis |
Medications | Reduce brain swelling, control BP | Mild to moderate cases |
Intensive Care Unit (ICU) | Continuous monitoring | Severe cases |
Surgical Drainage | Remove collected blood | Large or worsening bleeds |
Interventional Neurosurgery | Stop active bleeding | Selected cases |
Rehabilitation Therapy | Improve recovery | After stabilization |
Advanced care is usually provided in an intensive care unit (ICU) with close neurological monitoring.
Neurosurgery Care in Kadapa
- Access to timely neuro-emergency care is crucial in brain hemorrhage causes cases. Early diagnosis using CT scan brain or MRI brain and rapid decision-making significantly improve outcomes.
- In complex cases, care may involve an Interventional Neurosurgery Hospital in Kadapa, where minimally invasive procedures are used to control bleeding. A skilled Neurosurgeon in Kadapa evaluates each case to decide whether medical management or surgical intervention is required.
- Specialists like Dr. Kranthi Kumar Sunnepaneni play a key role in managing critical brain hemorrhage cases, combining clinical judgment with advanced neuro-imaging and surgical techniques.
Conclusion
- Brain hemorrhage causes are the medical emergency that demands fast recognition and immediate treatment. Early symptoms such as sudden headache, confusion, or loss of consciousness should never be ignored. Prompt diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and specialized neurological care can significantly reduce the risk of death and long-term disability.
- Recovery from brain hemorrhage causes varies depending on severity, age, and treatment timing. Some patients experience gradual improvement, while others may require long-term rehabilitation.
- For local information, directions, and patient reviews related to neurosurgical emergency care, you can visit the Google Business Profile of Vedanta Hospitals using the official Google listing link. This helps patients and families access verified local details quickly during emergencies.
FAQ'S
1. What is a brain hemorrhage?
A brain hemorrhage is a condition where bleeding occurs inside or around the brain due to a ruptured blood vessel. It is a serious type of hemorrhagic stroke that needs emergency care.
2. What are the main brain hemorrhage causes and symptoms?
Common brain hemorrhage causes and symptoms include sudden severe headache, vomiting, confusion, weakness on one side, and loss of consciousness. Symptoms usually appear suddenly and worsen fast.
3. Does brain hemorrhage causes brain bleeding?
Yes. Brain hemorrhage causes bleeding is commonly by high blood pressure, head injury, ruptured aneurysm, or weak blood vessels. Blood-thinning medicines can also increase risk.
4. Is brain hemorrhage the same as hemorrhagic stroke?
Yes, brain hemorrhage is a type of hemorrhagic stroke. It happens when a blood vessel bursts and causes bleeding in the brain instead of a blockage.
5. How is hemorrhage in brain diagnosed?
Doctors diagnose brain hemorrhage using a CT scan brain or MRI brain. These imaging tests show the location, size, and severity of brain bleeding.
6. Can hemorrhage cause death?
Yes, severe brain hemorrhage can cause death if not treated quickly. Early emergency treatment greatly improves survival chances.
7. What is intracerebral hemorrhage?
Intracerebral hemorrhage is bleeding that occurs directly inside the brain tissue. It is the most common type of brain hemorrhage and often linked to high blood pressure.
8. What is subarachnoid hemorrhage?
Subarachnoid hemorrhage is bleeding in the space between the brain and its covering layers. It usually causes a sudden, extremely severe headache and is often due to aneurysm rupture.
9. How long is brain hemorrhage recovery time?
Brain hemorrhage recovery time varies from weeks to months. It depends on the size of bleeding, patient age, and how quickly treatment was started.
10. Can brain hemorrhage recover without surgery?
Yes, mild brain hemorrhage cases may recover without surgery using medicines and close monitoring. Severe cases usually need surgical or interventional treatment.
11. Is brain hemorrhage more dangerous in old age?
Yes, brain hemorrhage old age cases are more dangerous because blood vessels are weaker and recovery is slower. Early detection is very important in elderly patients.
12. What happens during a brain hemorrhage emergency?
During a brain hemorrhage emergency, doctors focus on stabilizing the patient, controlling blood pressure, and reducing brain swelling. Treatment often starts in the intensive care unit (ICU).
13. What is the survival rate of brain hemorrhage?
The brain hemorrhage survival rate depends on how fast treatment begins, the type of hemorrhage, and overall health. Early care improves survival significantly.
14. Which scan is best for brain hemorrhage detection?
A CT scan brain is the fastest and most commonly used test to detect brain hemorrhage. MRI brain may be used later for detailed evaluation.
15. When should I go to the hospital for brain bleeding?
You should go to the hospital immediately if there is sudden headache, confusion, weakness, or loss of consciousness. Brain bleeding is a medical emergency and delays can be life-threatening.