BP, Diabetes & Hypertension:
Early Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore
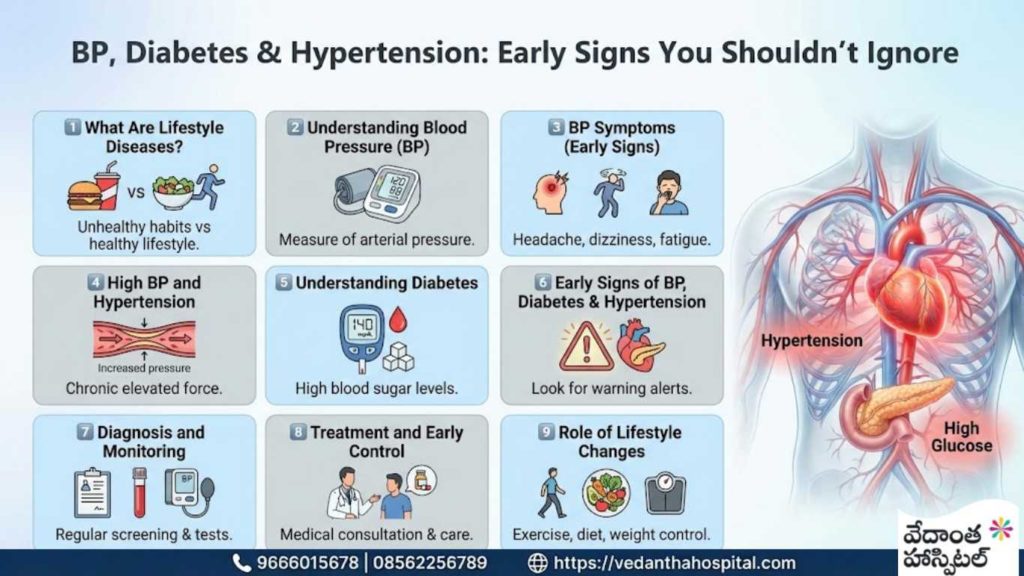
Lifestyle diseases like BP and Diabetes, also hypertension are no longer conditions seen only in older adults. Today, they affect people in their 30s and even 20s due to stress, poor diet, lack of exercise, and irregular health checkups. Early detection and timely control can prevent serious complications such as heart disease, kidney failure, stroke, and nerve damage.
This blog explains the early signs, causes, risks, diagnosis, and management of BP, diabetes, and hypertension, with a strong focus on prevention and long-term health.
What Are Lifestyle Diseases?
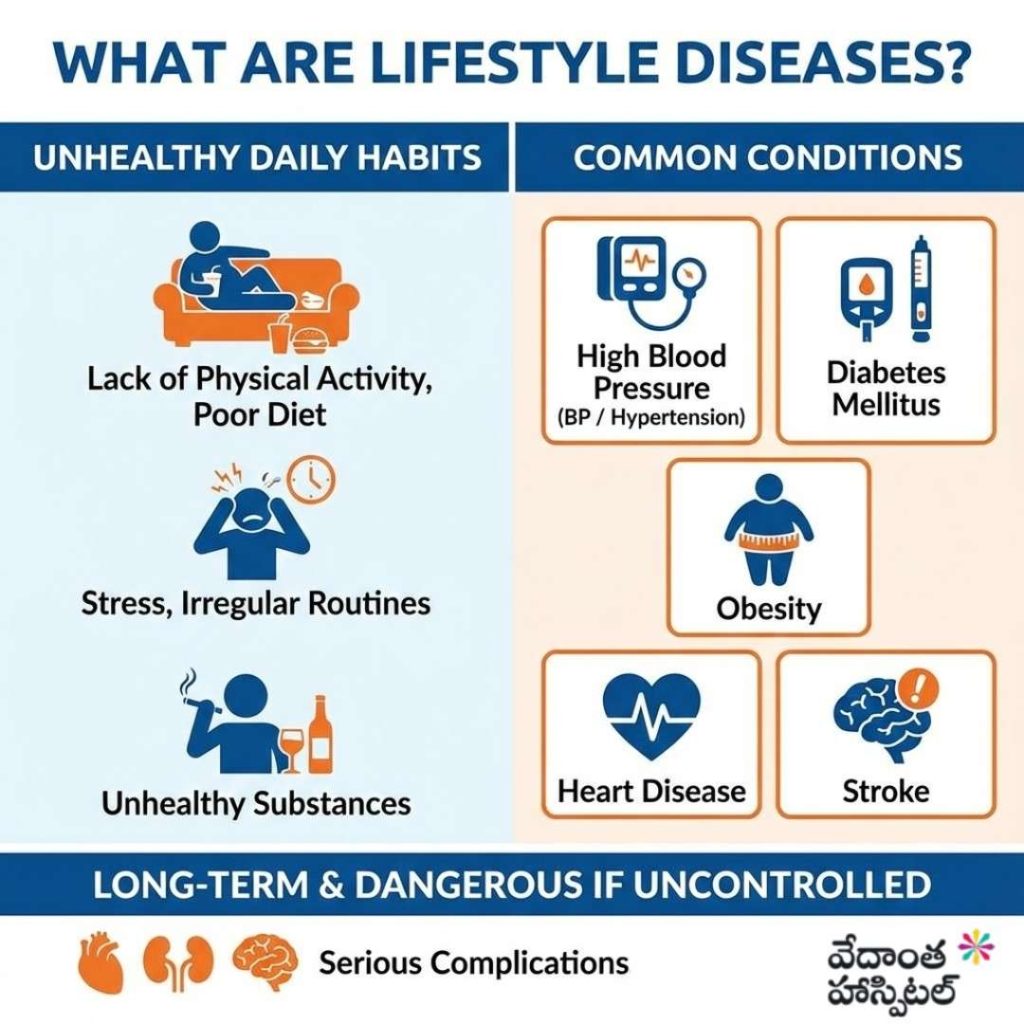
Lifestyle diseases are medical conditions that develop mainly due to unhealthy daily habits. Common lifestyle diseases include:
- High blood pressure (BP / Hypertension)
- Diabetes mellitus
- Obesity
- Heart disease
- Stroke
Among these, BP, diabetes, and hypertension are the most widespread and dangerous when left uncontrolled.
Lifestyle diseases are long-term health conditions that mainly develop due to unhealthy daily habits, stress, lack of physical activity, poor diet, and irregular routines. Common lifestyle diseases include high blood pressure (BP or hypertension), diabetes mellitus, obesity, heart disease, and stroke. Among these, BP, diabetes, and hypertension are the most widespread and dangerous, especially when they remain undiagnosed or poorly controlled for a long time, leading to serious complications affecting the heart, kidneys, brain, and overall quality of life.
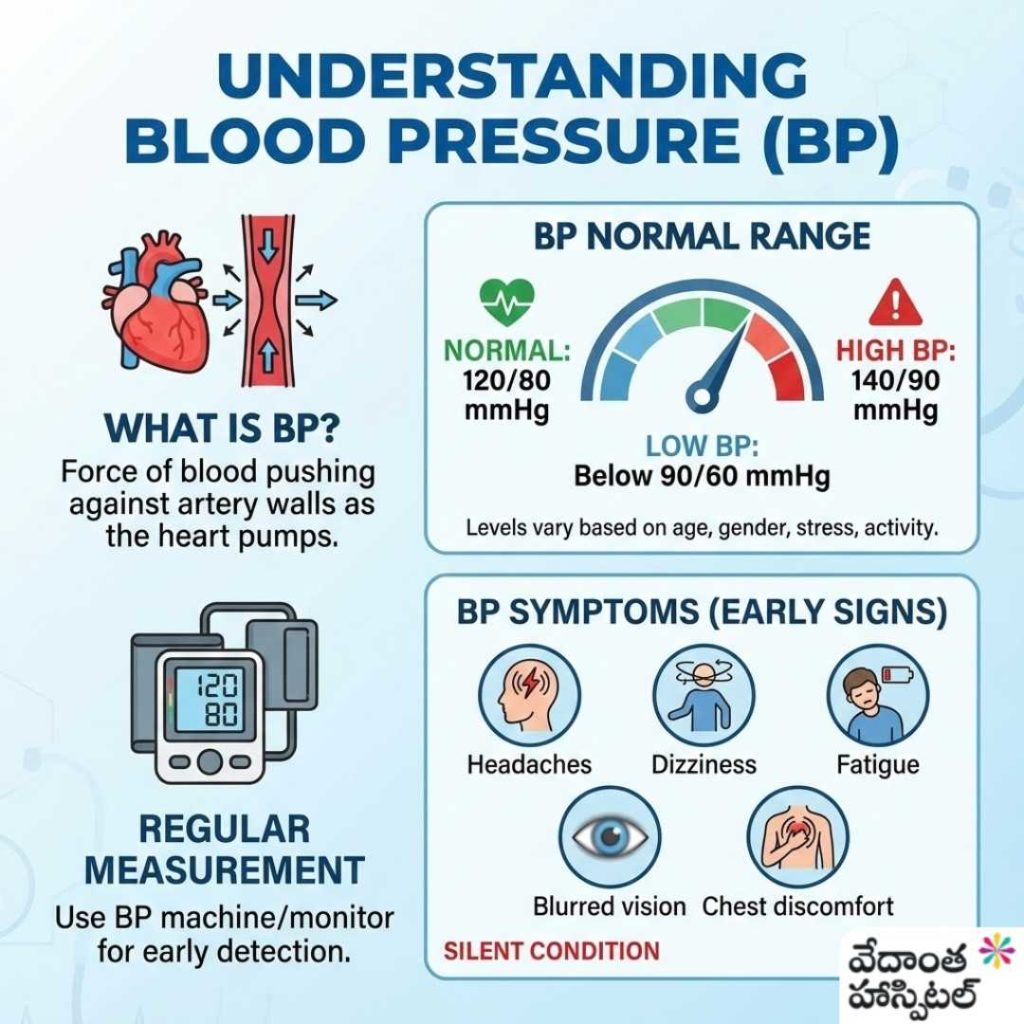
BP stands for Blood Pressure, which is the force of blood pushing against artery walls as the heart pumps blood.
BP Normal Range
- Normal BP: 120/80 mmHg
- BP 140/90: Considered high BP
- BP low range: Below 90/60 mmHg
BP levels vary based on age, gender, stress, and physical activity. Regular BP measurement using a BP machine or BP monitor helps detect problems early.
BP Symptoms (Early Signs)
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Chest discomfort
Many people with high BP show no symptoms, which is why it’s called a silent condition.
Understanding Blood Pressure (BP)
High BP and Hypertension Explained
Hypertension means persistently high blood pressure. It is medically referred to as hypertension high blood pressure.
Hypertension Normal Range
- Systolic BP: below 120
- Diastolic BP: below 80
High BP Reasons
- Excess salt intake
- Stress and anxiety
- Obesity
- Smoking and alcohol
- Lack of exercise
- Family history
Hypertension Types
- Primary hypertension
- Secondary hypertension
Hypertension Emergency
Severely high BP can lead to:
- Stroke
- Heart attack
Kidney failure
This is called a hypertension crisis and requires immediate medical care.
Understanding Diabetes
What Is Diabetes?
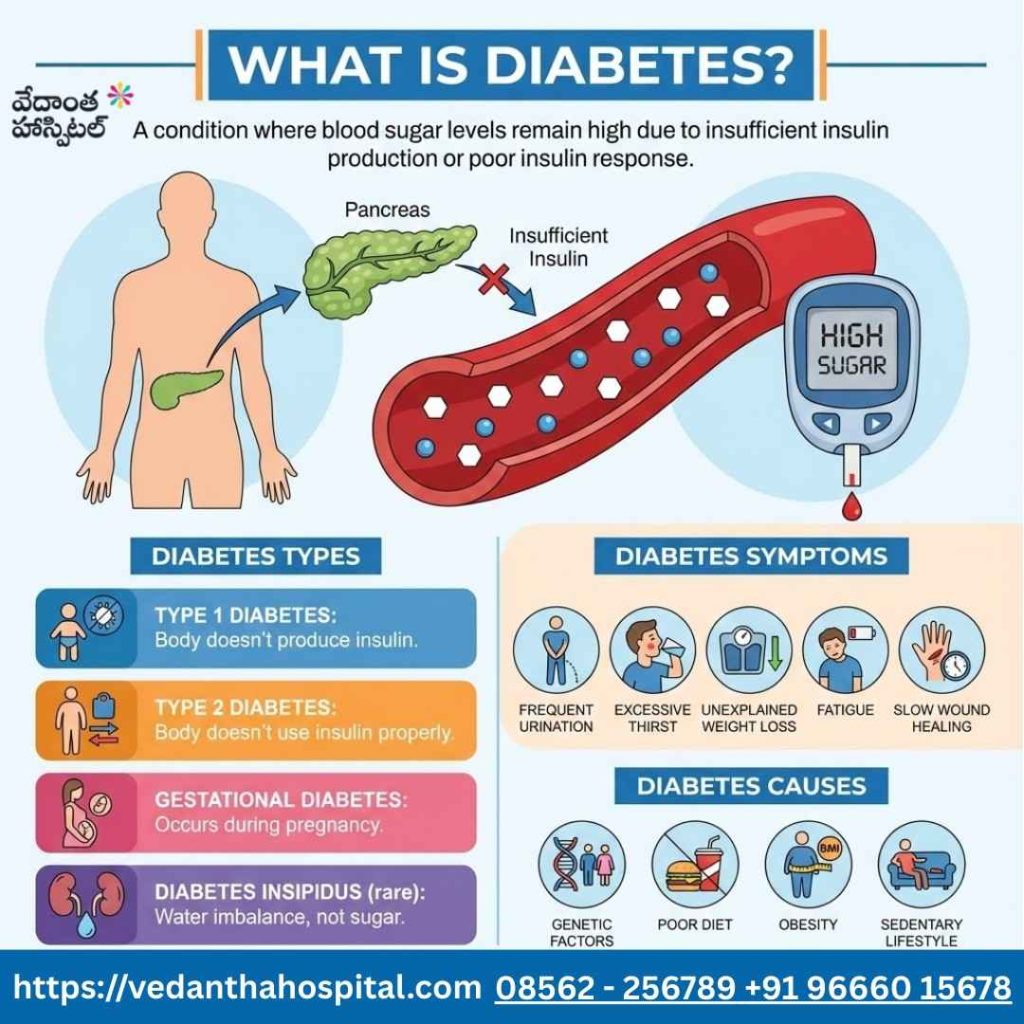
Diabetes is a condition where blood sugar levels remain high due to insufficient insulin production or poor insulin response.
Diabetes Types
- Type 1 diabetes
- Type 2 diabetes
- Gestational diabetes
- Diabetes insipidus (rare)
Diabetes Symptoms
- Frequent urination
- Excessive thirst
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Slow wound healing
Diabetes Causes
- Genetic factors
- Poor diet
- Obesity
- Sedentary lifestyle
BP and Diabetes: A Dangerous Combination
When BP and diabetes occur together, the risk of complications increases significantly. High blood sugar damages blood vessels, while high BP puts extra strain on the heart.
Possible complications include:
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Kidney damage
- Vision loss
- Nerve damage
Early care at a General Medicine Hospital in Kadapa can prevent long-term complications.
Table: Early Signs of BP, Diabetes & Hypertension
Condition | Early Signs | Risk If Ignored | Monitoring Method | When to See Doctor |
BP | Headache, dizziness | Stroke, heart attack | BP monitor | Persistent high readings |
High BP | Fatigue, chest pain | Hypertension crisis | Digital BP machine | BP >140/90 |
Diabetes | Thirst, urination | Kidney, nerve damage | Blood sugar test | Fasting sugar high |
Hypertension | Often silent | Organ damage | BP measurement | No symptoms but high BP |
BP & Diabetes | Weakness | Multiple organ failure | Regular tests | Early diagnosis needed |
Diagnosis and Monitoring of
BP and Diabetes
BP Measurement
- Digital BP machine
- Manual BP monitor
- Home BP monitoring
Diabetes Tests
- Fasting blood sugar
- HbA1c
- Random blood sugar
Regular screening is advised, especially for adults above 30.
Role and Lifestyle Changes of
BP and Diabetes
A healthy lifestyle plays a key role in controlling BP, diabetes, and hypertension at an early stage. Small daily habits can make a big difference:
- Healthy diet (low salt, low sugar)
- Daily exercise
- Weight control
- Adequate sleep
- Avoid smoking and alcohol
- Stress management
- Regular health check-ups
Lifestyle correction is the foundation of early control.
Treatment and Early Control of BP and Diabetes
High BP Treatment
- Lifestyle changes
- High BP drugs (if required)
- Stress management
- Salt reduction
Diabetes Treatment
- Diet control
- Physical activity
- Diabetes medication
- Regular follow-ups
Hypertension Treatment
- BP control medicines
- Weight management
- Regular monitoring
Early treatment reduces the risk of emergencies and hospitalizations.
Expert Care in Kadapa
- Patients seeking early diagnosis and management can consult experienced physicians at Vedanta Hospitals in Kadapa, a trusted Multispeciality Hospital in Kadapa.
- Under the guidance of Dr. Sree Madhurya M, patients receive comprehensive care for BP, diabetes, and hypertension with a preventive approach.
- As a leading General Medicine Hospital in Kadapa, Vedanta focuses on long-term disease control rather than temporary relief.
Conclusion
- BP, diabetes, and hypertension are silent but dangerous lifestyle diseases. Ignoring early signs can lead to lifelong complications. The key lies in early detection, regular monitoring, and lifestyle correction.
- With timely care at Vedanta Hospitals in kadapa, patients can manage these conditions effectively and lead a healthier life.
FAQ'S
1. What are the early symptoms of high BP?
High BP often has no symptoms, but some people experience headaches, dizziness, or tiredness. Regular BP checks are important to detect it early.
2. Can BP and diabetes occur together?
Yes, BP and diabetes commonly occur together and increase the risk of heart, kidney, and eye problems if not controlled early.
3. What BP range is considered normal?
A normal BP range is around 120/80 mmHg. Readings consistently above 140/90 mmHg are considered high BP.
4. What are common diabetes symptoms to watch for?
Common diabetes symptoms include frequent urination, increased thirst, tiredness, and unexplained weight loss.
5. What causes high BP in young adults?
High BP in young adults can be caused by stress, obesity, lack of exercise, high salt intake, and family history.
6. Is hypertension the same as high blood pressure?
Yes, hypertension is the medical term for high blood pressure, especially when BP stays high over a long period.
7. How can BP be controlled naturally?
BP can be controlled by reducing salt intake, exercising regularly, managing stress, and maintaining a healthy weight.
8. What is the normal BP range for men and women?
Normal BP range for both men and women is below 120/80 mmHg, though slight variations may occur with age.
9. How is diabetes diagnosed early?
Diabetes is diagnosed using blood tests like fasting blood sugar, post-meal sugar, and HbA1c levels.
10. What happens if BP and diabetes are not treated early?
Untreated BP and diabetes can lead to heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, vision loss, and nerve damage.