Brain Stroke Symptoms: Recognise the Warning Signs
- A brain stroke is one of the most serious medical emergencies, occurring when blood flow to part of the brain is suddenly interrupted. Without oxygen, brain cells start dying within minutes — which can lead to permanent disability or even death. The ability to identify Brain Stroke Symptoms early and seek timely care is often what saves a life.
- Every minute counts. Across India, awareness of these warning signs remains low, leading to delayed hospital visits. Quick diagnosis and treatment, especially through modern interventional neurosurgery, can significantly improve recovery chances.
- This article explains in simple language what a brain stroke is, how to recognise early signs, and what treatments are available in advanced facilities such as any qualified Neurosurgery Hospital in Kadapa or a specialized Interventional Neurosurgery Hospital in Kadapa.

What Is a Brain Stroke?
A brain stroke, also known as a “brain attack,” happens when the blood supply to the brain is blocked or when a blood vessel bursts, causing bleeding inside or around the brain. Because the brain depends on a constant flow of oxygenated blood, any interruption quickly injures brain tissue.
There are two primary types:
- Ischemic stroke – caused by a clot that blocks blood flow.
- Hemorrhagic stroke – caused by bleeding in or around the brain.
A temporary event called a Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA), or “mini-stroke,” occurs when the blockage clears quickly but still warns of serious risk.
People treated at a modern Brain Surgery Hospital in Kadapa can now receive clot-removal procedures and targeted therapies that restore circulation far faster than ever before.
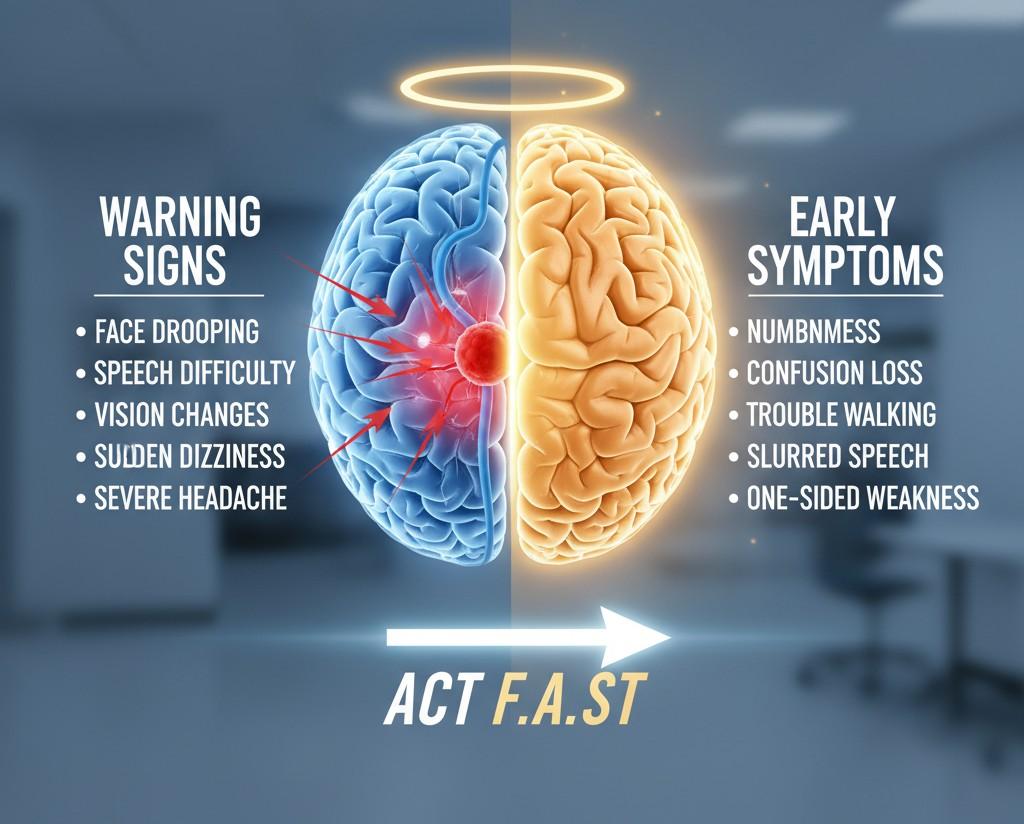
Brain Stroke Warning Signs and Early Symptoms
Recognising Brain Stroke Symptoms within the first few minutes is crucial. Specialists worldwide use the acronym FAST to help people remember the signs:
- F – Face drooping: One side of the face suddenly feels weak or looks uneven.
- A – Arm weakness: Inability to raise one arm fully.
- S – Speech difficulty: Slurred or confusing speech.
- T – Time to act: Call emergency services immediately.
Other Brain Stroke Symptoms can include:
- Sudden loss of balance or coordination
- Vision problems in one or both eyes
- Numbness or tingling on one side of the body
- Sudden severe headache with no known cause
- Dizziness or fainting
If you notice these warning signs in yourself or someone else, don’t delay. Reaching a Vedanta Hospital in Kadapa or any emergency-ready Neurosurgery Hospital in Kadapa within the “golden hours” (first 4.5 hours) can determine how well the brain recovers.
Causes and Detailed Symptoms of Brain Stroke
Several factors contribute to stroke. Some are lifestyle-related, while others involve medical conditions:
Major Causes
- High blood pressure: The most common trigger; it damages arteries and causes them to rupture or narrow.
- Blood clots: Formed due to high cholesterol or irregular heartbeat (atrial fibrillation).
- Diabetes: Affects small blood vessels and thickens artery walls.
- Smoking and alcohol: Reduce oxygen in the blood and weaken vessel walls.
- Stress and inactivity: Increase the chance of obesity and poor circulation.
- Genetic predisposition: A family history of stroke raises risk.
Symptoms
- Weakness or paralysis on one side of the body
- Trouble speaking or understanding words
- Sudden confusion, dizziness, or loss of balance
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing
- Blurred or double vision
- Severe unexplained headache
Doctors at an Interventional Neurosurgery Hospital in Kadapa use brain imaging (CT or MRI scans) to confirm the cause quickly and decide the right treatment path.
Types of Brain Stroke
Type | What Happens | Main Cause | Treatment Approach |
Ischemic Stroke | A clot blocks blood flow to a part of the brain. | Atherosclerosis, embolism, or thrombosis. | Clot-busting drugs (tPA), mechanical thrombectomy (catheter removal). |
Hemorrhagic Stroke | A blood vessel bursts, causing internal bleeding. | Hypertension, aneurysm rupture, trauma. | Surgery to stop bleeding, clip or coil aneurysm, reduce brain pressure. |
Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) | A brief blockage with temporary symptoms. | Spasms or micro-clots that dissolve. | Medications, lifestyle control, monitoring to prevent full stroke. |
Each type shows similar Brain Stroke Symptoms but demands different medical responses. Only trained neurosurgeons at a specialized Brain Surgery Hospital in Kadapa can identify which type is occurring.

Brain Stroke Risk Factors
Some factors are unchangeable — such as age or genetics — but most are controllable with lifestyle changes:
Uncontrollable Factors
- Age over 55
- Family history of stroke
- Previous stroke or TIA
- Certain hereditary clotting disorders
Controllable Factors
- High blood pressure and cholesterol
- Diabetes and obesity
- Smoking or heavy alcohol use
- Sedentary lifestyle
- High stress levels
Regular check-ups at multi-specialty centres like Vedanta Hospital in Kadapa help monitor these risks and detect problems before they lead to a stroke.
Treatment Options for Brain Stroke
Treatment Type | Purpose | When Used | Outcome |
Thrombolysis (Clot-Busting Drugs) | Dissolve clots blocking blood flow in ischemic strokes. | Within 4.5 hours of onset. | Restores circulation, prevents further brain damage. |
Mechanical Thrombectomy | A thin catheter removes the clot. | Large artery blockages (up to 6 hours). | Immediate improvement in symptoms. |
Aneurysm Coiling/Clipping | Stops bleeding and seals ruptured vessels. | Hemorrhagic strokes or aneurysms. | Reduces re-bleeding risk. |
Medication Therapy | Controls blood pressure, cholesterol, and clotting. | During recovery and prevention stages. | Prevents recurrence. |
Neuro-Rehabilitation | Physical, speech, and occupational therapy. | After stabilization. | Helps regain movement and independence. |
Lifestyle Modification | Diet, exercise, smoking cessation. | Continuous. | Long-term prevention of future strokes. |
Many of these procedures are available in advanced Interventional Neurosurgery Hospitals in Kadapa, where doctors combine imaging technology with catheter-based surgery to treat the problem without open brain operations.
Prevention: How to Prevent a Brain Stroke
Most strokes are preventable.
- Control hypertension with medication and lifestyle adjustment.
- Check cholesterol levels regularly.
- Treat heart conditions like atrial fibrillation early.
- Maintain healthy weight and stay active.
- Avoid smoking and limit salt intake.
- Know your family history to manage genetic risks.
Preventive awareness campaigns by hospitals such as Vedanta Hospital in Kadapa and similar regional centers aim to educate families about these steps.
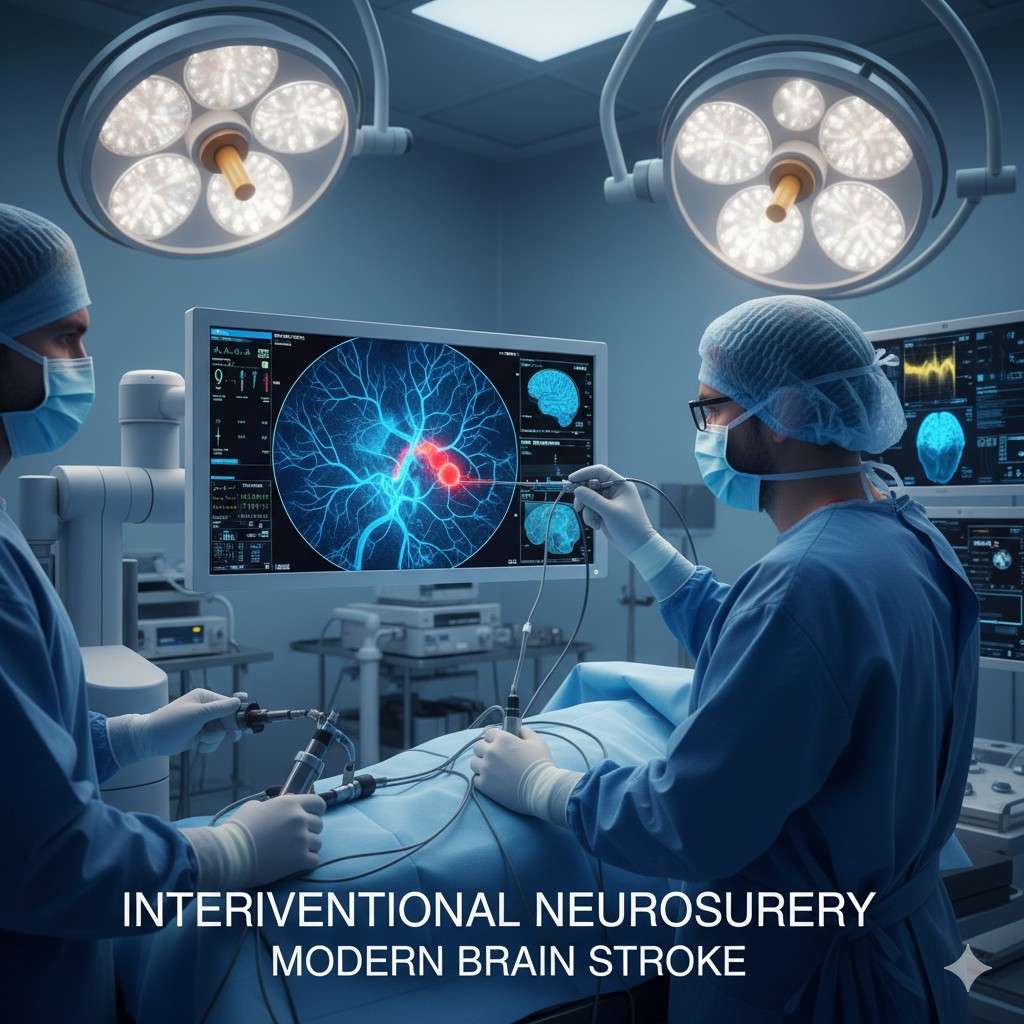
Interventional Neurosurgery in Modern Brain Stroke
Common Interventional Techniques
- Mechanical Thrombectomy: Physically removing the clot from a blocked artery.
- Aneurysm Coiling: Filling weak blood vessels with tiny coils to prevent rupture.
- Stent Placement: Reinforcing artery walls to keep them open.
- Embolization: Blocking abnormal blood vessels to stop bleeding.
These minimally invasive procedures reduce recovery time and complications. Hospitals equipped for such care — like an Interventional Neurosurgery Hospital in Kadapa — can handle emergencies 24×7 with highly trained teams.

Brain Stroke Symptoms: Recognise the Warning Signs
- Recognising Brain Stroke Symptoms early saves lives. Acting within the first few hours can mean the difference between full recovery and long-term disability.
While anyone can experience a stroke, most risk factors are preventable through healthy living, timely check-ups, and awareness. - Modern medicine — especially interventional neurosurgery — has transformed stroke care by offering precise, minimally invasive treatments. If you ever notice warning signs, seek medical help at the nearest emergency department or a qualified Neurosurgery Hospital in Kadapa without delay.
- Education and timely action remain the most powerful tools in preventing brain strokes and ensuring a healthier future for all.
Our Relevant Blogs
FAQ'S
1. What are the early symptoms of a brain stroke?
Early Brain Stroke Symptoms include sudden weakness, facial drooping, slurred speech, and severe headache. Acting fast can prevent permanent brain damage.
2. How quickly must you treat a brain stroke?
Doctors must begin treatment within 4.5 hours for best outcomes. Rapid care in an Interventional Neurosurgery Hospital in Kadapa can reverse most effects.
3. What causes brain stroke in adults?
High blood pressure, diabetes, smoking, and high cholesterol are major causes. Regular monitoring helps reduce the risk.
4. Can interventional neurosurgery treat stroke?
Yes, it can remove clots, repair vessels, and stop internal bleeding — often with small punctures instead of open surgery.
5. How long does recovery take after a brain stroke?
Recovery time depends on stroke severity and therapy. Some recover within weeks; others may need months of rehabilitation.
6. What warning signs mean you may be having a brain stroke?
Sudden numbness, speech difficulty, blurred vision, and loss of coordination are major warning signs. Visit a Neurosurgery Hospital in Kadapa immediately.
7. Can brain stroke treatment without surgery work?
Yes. For ischemic strokes, medications like tPA or blood thinners often restore blood flow without surgery.
8. Are there different types of brain strokes?
Three main types exist: ischemic, hemorrhagic, and transient ischemic attack (TIA). Each requires specific treatment.
9. How can I prevent brain stroke naturally?
Eat healthy, exercise, reduce salt, and avoid smoking or alcohol. Managing stress also helps protect blood vessels.
10. Where can I get advanced brain stroke treatment in Kadapa?
Patients can receive emergency stroke management and neuro-rehabilitation at multi-specialty centers or a Brain Surgery Hospital in Kadapa equipped with imaging and interventional facilities.