Difference Between Cardiac Arrest and Heart Attack
Heart-related emergencies are among the leading causes of sudden death worldwide. Two terms that often confuse people are cardiac arrest and heart attack. Although they are related to the heart, they are not the same condition. Understanding the Difference Between Cardiac Arrest and Heart Attack can save lives, especially when early action is taken.
At a Cardiology Hospital in Kadapa, doctors often see patients arriving late simply because they did not recognize the warning signs correctly. This article explains the difference in simple language, covering causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.

- Many people use the terms cardiac arrest and heart attack interchangeably, but medically they are very different.
A heart attack is primarily a circulation problem, while cardiac arrest is an electrical problem of the heart. - Knowing the Difference Between Cardiac Arrest and Heart Attack helps families respond faster and seek the right emergency care from a Cardiologist or a Cardiothoracic Surgery Hospital in Kadapa.
What Is Cardiac Arrest?
- Cardiac arrest occurs when the heart suddenly stops beating effectively. This happens due to a malfunction in the heart’s electrical system, causing irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias).
- Cardiac arrest means the heart cannot pump blood to the brain and vital organs, leading to loss of consciousness and sudden collapse.
- A sudden cessation of heart function, breathing, and consciousness.
- It is a medical emergency requiring immediate CPR and defibrillation.
Common cardiac arrest causes
- Abnormal heart rhythm (ventricular fibrillation)
- Cardiopulmonary arrest
- Severe heart disease
- Untreated heart attack
- Congenital heart disorders
- Electrolyte imbalance
- Drug overdose
Cardiac arrest disease can affect people of all ages and often occurs without warning.

What Is a Heart Attack?

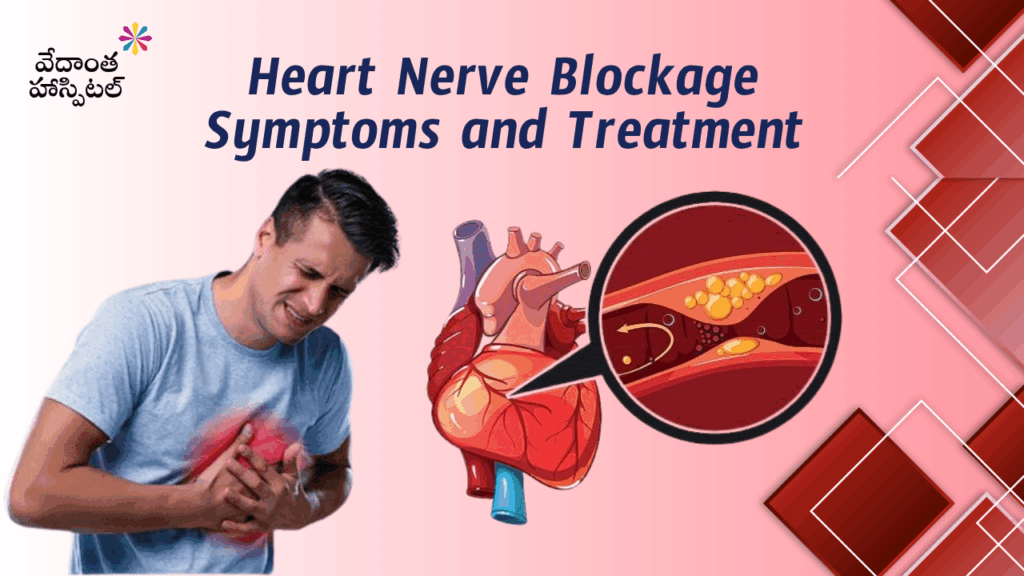
- A heart attack (myocardial infarction) occurs when blood flow to part of the heart muscle is blocked, usually due to a clot in a coronary artery.
Damage to the heart muscle caused by reduced blood supply.
Heart attack causes
- Blocked coronary arteries
- High cholesterol
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Obesity
Unlike cardiac arrest, many heart attacks allow the person to remain conscious, especially in early stages.
Difference Between Cardiac Arrest and Heart Attack
Feature | Cardiac Arrest | Heart Attack |
Primary problem | Electrical malfunction | Blood flow blockage |
Heart beating | Stops suddenly | Usually continues |
Consciousness | Immediate loss | Often conscious |
Emergency response | CPR + defibrillator | Emergency medicines, angioplasty |
Survival depends on | Immediate response | Speed of hospital care |
This table clearly explains the Difference Between Cardiac Arrest and Heart Attack in a practical way.
What Happens During Cardiac Arrest and Heart Attack
During Cardiac Arrest
- Heart rhythm becomes chaotic
- Blood circulation stops
- Brain damage begins within minutes
- Death occurs without immediate treatment
During a Heart Attack
- Heart muscle is starved of oxygen
- Chest pain develops
- Damage increases over time
- Timely treatment can save heart muscle
Many cardiac arrest cases actually begin as heart attacks, which is why early treatment is critical at a Cardiology Hospital in Kadapa.
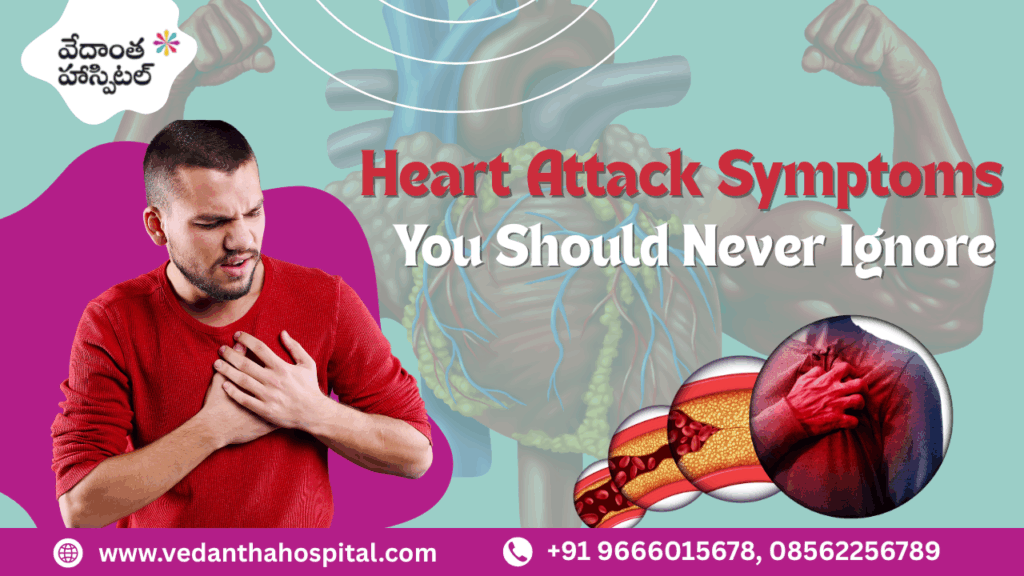
Warning Signs You Should Never Ignore
Many patients ignore early signs thinking they are gas pain or stress.
Heart attack warning signs
- Persistent chest discomfort
- Pain spreading to left arm
- Sudden fatigue
- Heart attack blood test abnormalities
Cardiac arrest warning signs
- Fainting episodes
- Palpitations
- Severe dizziness
- Family history of sudden death
Recognizing these signs early can prevent progression to cardiopulmonary arrest.
Common Symptoms of
Cardiac Arrest and Heart Attack
Cardiac Arrest Symptoms
- Sudden collapse
- No pulse
- No breathing
- Loss of consciousness
Heart Attack Symptoms
- Chest pain or pressure
- Heart attack pain location (center or left chest)
- Heart attack pain area (chest, arm, jaw, back)
- Sweating
- Nausea
- Shortness of breath
Heart attack symptoms may differ in women and elderly patients, which makes awareness even more important.

Diagnosis and Tests of Heart Attack and Cardiac Arrest
For Heart Attack
- ECG
- Heart attack blood test (Troponin)
- Coronary angiography
For Cardiac Arrest
- Clinical assessment
- ECG rhythm analysis
- Cause identification after stabilization
At a Cardiology Hospital in Kadapa, diagnosis is often guided by experienced specialists like Dr. Sravan Kumar Nandaluru, Senior Interventional Cardiologist.
Treatment Options
Cardiac Arrest Treatment
- Immediate CPR
- Defibrillation
- Advanced life support
- ICU monitoring
Heart Attack Treatment
- Heart attack emergency tablet (as advised)
- Heart attack drugs
- Angioplasty and stenting
- Bypass surgery at a Cardiothoracic Surgery Hospital
Early treatment significantly improves survival and recovery.
Preventing Cardiac Arrest and Heart Attack
Lifestyle Prevention
- Control blood pressure
- Manage cholesterol
- Quit smoking
- Regular exercise
- Healthy diet
Medical Prevention
- Regular heart checkups
- ECG screening
- Stress management
- Medication adherence
Prevention programs at an Cardiology Hospital help reduce long-term risks.
FAQ'S
1. What is the difference between cardiac arrest and heart attack?
A heart attack occurs when blood flow to the heart is blocked, causing damage. Cardiac arrest, on the other hand, is when the heart stops beating due to electrical disturbances, leading to sudden loss of consciousness.
2. Can cardiac arrest be prevented?
While some risk factors for cardiac arrest cannot be controlled, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing blood pressure, and regular exercise can help prevent it. Early defibrillation can save lives during an emergency.
3. What are the signs of cardiac arrest?
Signs of cardiac arrest include sudden collapse, no pulse, no breathing, and loss of consciousness. If you notice these symptoms, it is critical to start CPR immediately and call emergency services.
4. Can a heart attack lead to cardiac arrest?
Yes, a heart attack can lead to cardiac arrest. When a heart attack causes significant damage to the heart muscle, it can trigger electrical disturbances that lead to cardiac arrest.
5. How is a heart attack diagnosed?
A heart attack is diagnosed using blood tests, an ECG (electrocardiogram), and imaging tests such as a coronary angiogram to evaluate the condition of the heart and blood vessels.
6. How long can someone survive after cardiac arrest without treatment?
Without immediate treatment, such as CPR or defibrillation, survival rates for cardiac arrest are extremely low. The chances of survival drop by about 10% for each minute that passes without intervention.
7. Can cardiac arrest happen without warning?
Cardiac arrest can occur suddenly, without warning, especially in individuals with underlying heart conditions. However, there may be signs such as chest discomfort or shortness of breath prior to the event.
8. What is the first aid for heart attack?
If someone is experiencing a heart attack, first aid includes calling emergency services, having the person chew and swallow an aspirin (if not allergic), and keeping them calm and still until help arrives.
9. How do you treat cardiac arrest?
The primary treatment for cardiac arrest is immediate CPR to maintain blood flow, followed by defibrillation with an AED (Automated External Defibrillator) to restore the heart’s rhythm.
10. What is the survival rate for cardiac arrest?
The survival rate for cardiac arrest depends on how quickly CPR is started and defibrillation is administered. Immediate action can increase the survival rate significantly, though overall rates are still low, especially outside a hospital setting.
11. Is cardiac arrest the same as heart failure?
No, cardiac arrest is the sudden loss of heart function, while heart failure is a long-term condition where the heart is unable to pump blood efficiently. Cardiac arrest is an emergency situation that can occur in individuals with heart failure.
12. What is the role of defibrillation in cardiac arrest?
Defibrillation is a critical treatment for cardiac arrest. It uses an electric shock to restore the heart’s normal rhythm. This is essential in cases where the heart is experiencing an abnormal rhythm like ventricular fibrillation.
13. Can a heart attack be fatal?
Yes, heart attacks can be fatal if the damage to the heart is extensive or if timely treatment is not provided. Early recognition and intervention are key to improving survival rates.
14. How can heart attacks be prevented?
Heart attacks can be prevented by managing risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, and maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise. Regular check-ups at a Cardiology Hospital in Kadapa can help monitor these factors.
15. What are the stages of a heart attack?
A heart attack progresses in stages, starting with ischemia (reduced blood flow), followed by injury (damage to the heart muscle), and finally infarction (tissue death). Immediate medical attention is crucial to limit damage.