Migraine vs Normal Headache
Headaches are one of the most common health complaints worldwide. Almost everyone experiences a headache at some point in life. However, not all headaches are the same. Many people confuse a migraine with a normal headache, which often leads to delayed diagnosis and improper treatment.
Understanding the difference between migraine vs normal headache is important because migraines are neurological conditions that require specific care, while normal headaches are usually temporary and less severe. Early identification can prevent complications and improve quality of life.
This article explains the differences in a simple, clear way—covering symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment options, and when to seek medical help.
What Is a Normal Headache?
A normal headache, also called a tension-type headache, is the most common type of headache. It usually occurs due to stress, fatigue, dehydration, poor posture, or lack of sleep.
Common Characteristics of a Normal Headache:
- Mild to moderate pain
- Tight or pressing sensation around the head
- Pain on both sides of the head
- No nausea or vomiting
- Does not worsen with physical activity
Normal headaches often go away with rest, hydration, or simple pain relievers. They usually do not interfere significantly with daily activities.
People visiting a General Medicine Hospital commonly report such headaches, especially due to work stress or lifestyle issues.
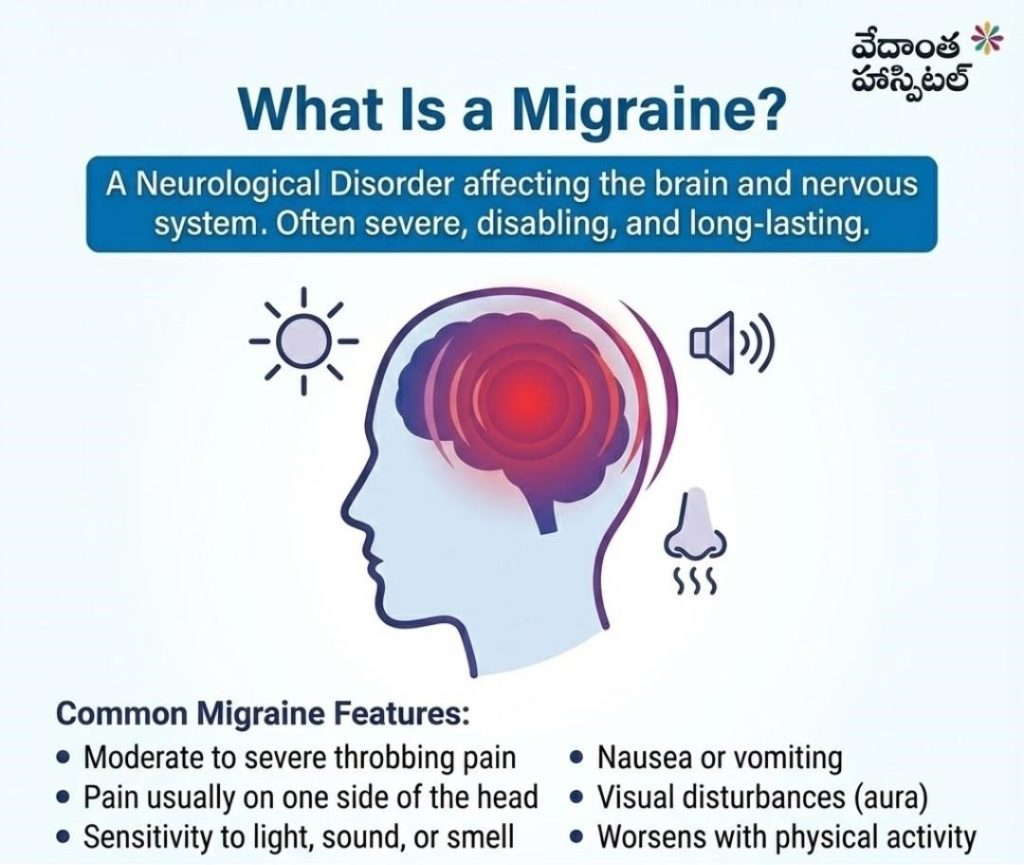
What Is a Migraine?
A migraine is a neurological disorder, not just a headache. It affects the brain and nervous system and often occurs repeatedly. Migraines can be severe, disabling, and long-lasting.
Common Migraine Features:
- Moderate to severe throbbing pain
- Pain usually on one side of the head
- Sensitivity to light, sound, or smell
- Nausea or vomiting
- Visual disturbances (aura)
- Worsens with physical activity
Migraines can last from a few hours to several days and may require specialized neurological evaluation at a Neurosurgery Hospital in Kadapa or an Interventional Neurosurgery Hospital if symptoms are severe or recurring.
Migraine vs Normal Headache – Key Differences
|
Feature |
Normal Headache |
Migraine |
|
Pain Type |
Dull, pressure-like |
Throbbing or pulsating |
|
Pain Location |
Both sides |
Usually one side |
|
Severity |
Mild to moderate |
Moderate to severe |
|
Nausea |
Rare |
Common |
|
Light/Sound Sensitivity |
Rare |
Common |
|
Duration |
Few hours |
Hours to days |
|
Physical Activity Effect |
No change |
Pain worsens |
|
Neurological Symptoms |
No |
Yes (aura, vision issues) |
This comparison helps patients understand why migraines should not be ignored.

Symptoms That Should Not Be Ignored
Some headache symptoms require immediate medical attention.
Warning Signs:
- Sudden severe headache
- Headache with weakness or numbness
- Headache with vision loss
- Headache after head injury
- Persistent headache with vomiting
- Headache with confusion or speech difficulty
These symptoms may indicate conditions related to the brain or spine and should be evaluated at a Brain Surgery Hospital or Spine Surgery Hospital.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Diagnosis:
Doctors may recommend:
- Detailed medical history
- Neurological examination
- Blood tests
- MRI or CT scan (if needed)
Advanced imaging and neurological assessments are available at a Multispeciality Hospital in Kadapa, ensuring accurate diagnosis.
Treatment for Normal Headache:
- Adequate rest
- Hydration
- Stress management
- Over-the-counter pain relievers
- Posture correction
Treatment for Migraine:
- Preventive medications
- Pain-relief medicines
- Lifestyle modifications
- Trigger avoidance
- Neurological consultation
For severe or chronic migraines, evaluation at an Interventional Neurosurgery Hospital or Neurosurgery Hospital may be required.
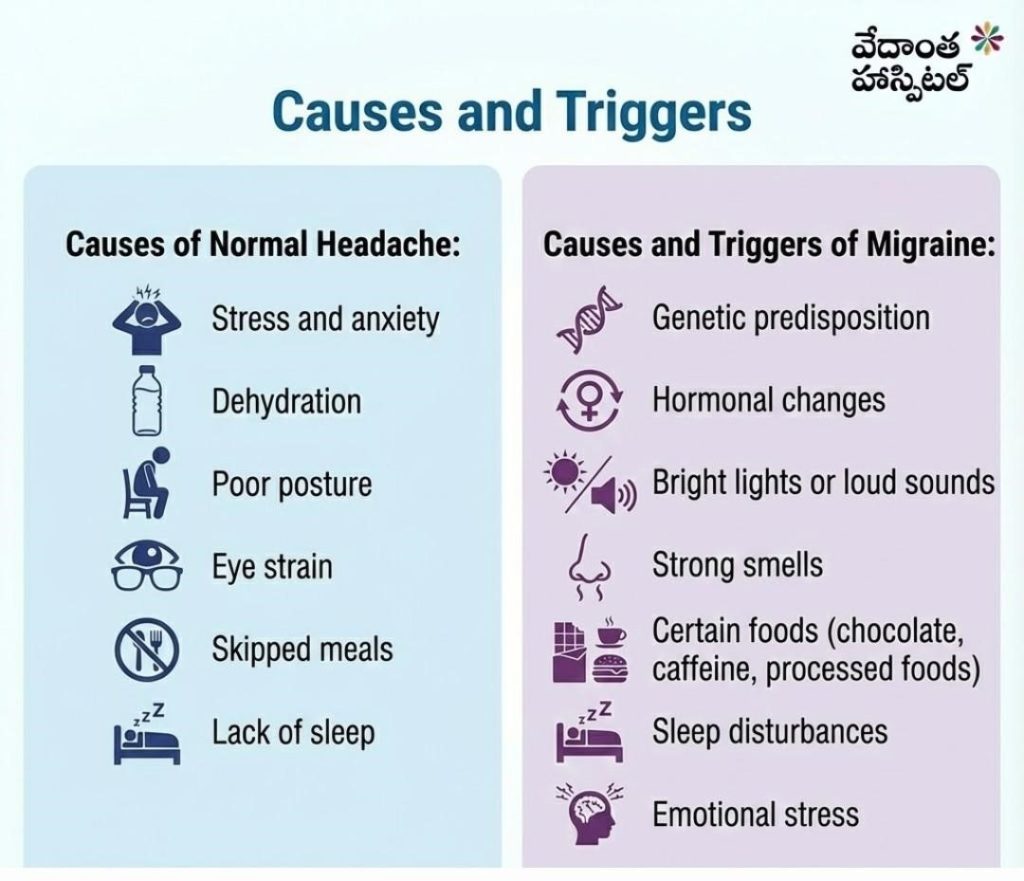
Causes and Triggers of Migraine and Normal Headache
Causes of Normal Headache:
- Stress and anxiety
- Dehydration
- Poor posture
- Eye strain
- Skipped meals
- Lack of sleep
These headaches are often managed by lifestyle changes and are commonly treated in a General Medicine Hospital in Kadapa.
Causes and Triggers of Migraine:
- Genetic predisposition
- Hormonal changes
- Bright lights or loud sounds
- Strong smells
- Certain foods (chocolate, caffeine, processed foods)
- Sleep disturbances
- Emotional stress
Migraines may involve changes in brain chemicals and nerve pathways, which is why neurological evaluation is important.
When to See a Doctor if you are having Migraine or Normal Headache
You should consult a doctor if:
- Headaches occur frequently
- Pain is worsening over time
- Headache affects daily life
- Medications are ineffective
- Neurological symptoms appear
People with associated heart symptoms may need evaluation at a Cardiology Hospital in Kadapa, while spine-related nerve pain may require a Spine Surgery or Orthopedic Hospital.
Associated Conditions That May Mimic Headaches
Sometimes headaches are linked to other medical conditions such as:
- Cervical spine issues
- Blood pressure problems
- Sinus infections
- Nerve compression
- Cardiac-related referred pain
Comprehensive evaluation at a Multispeciality Hospital in Kadapa helps identify the true cause and ensures appropriate treatment.
Understanding migraine vs normal headache helps people seek the right care at the right time. While normal headaches are usually harmless and temporary, migraines can significantly affect quality of life if ignored.
Early diagnosis, lifestyle changes, and appropriate medical care can prevent complications. If headaches are persistent, severe, or associated with other symptoms, professional evaluation is essential.
FAQ'S
1. Is migraine more serious than a normal headache?
Yes, migraine is a neurological condition and often more severe.
2. Can stress cause migraine?
Yes, stress is a common trigger for migraines.
3. How long does a migraine last?
Migraines can last from a few hours to several days.
4. Do migraines require brain scans?
Only if symptoms are severe, unusual, or worsening.
5. Can posture cause headaches?
Poor posture commonly causes normal headaches and neck pain.
6. Are migraines hereditary?
Yes, migraines often run in families.
7. Can heart problems cause headaches?
In rare cases, yes – especially related to blood pressure issues.
8. Can spine problems cause headaches?
Yes, cervical spine issues can trigger headaches.
9. Is vomiting common in migraine?
Yes, nausea and vomiting are common migraine symptoms.
10. When should I see a neurologist?
If headaches are frequent, severe, or associated with neurological symptoms.
11. Can stress cause migraines?
Yes, stress is a common trigger for migraines. Emotional stress can lead to the release of chemicals in the brain that contribute to the onset of a migraine.
12. Can dehydration cause a migraine?
Dehydration is a known trigger for migraines. When the body is dehydrated, it can lead to reduced blood flow and electrolyte imbalances, which can provoke a migraine attack.
13. Are migraines hereditary?
Yes, migraines tend to run in families. If one or both parents suffer from migraines, there’s a higher likelihood that their children may experience them as well.
14. Can weather changes trigger migraines?
Yes, changes in weather, such as fluctuations in temperature, humidity, or barometric pressure, can trigger migraines in some individuals due to their effect on the brain’s blood vessels.
15. What is the difference between a tension headache and a migraine?.
A tension headache is typically caused by muscle tightness in the neck and scalp, while a migraine is often associated with more intense, throbbing pain, nausea, and light sensitivity.