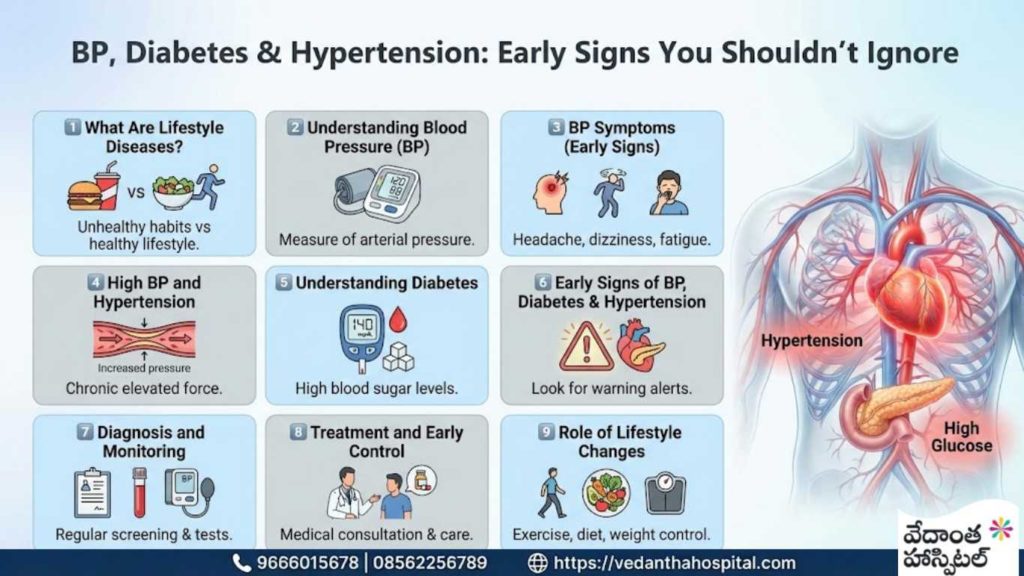
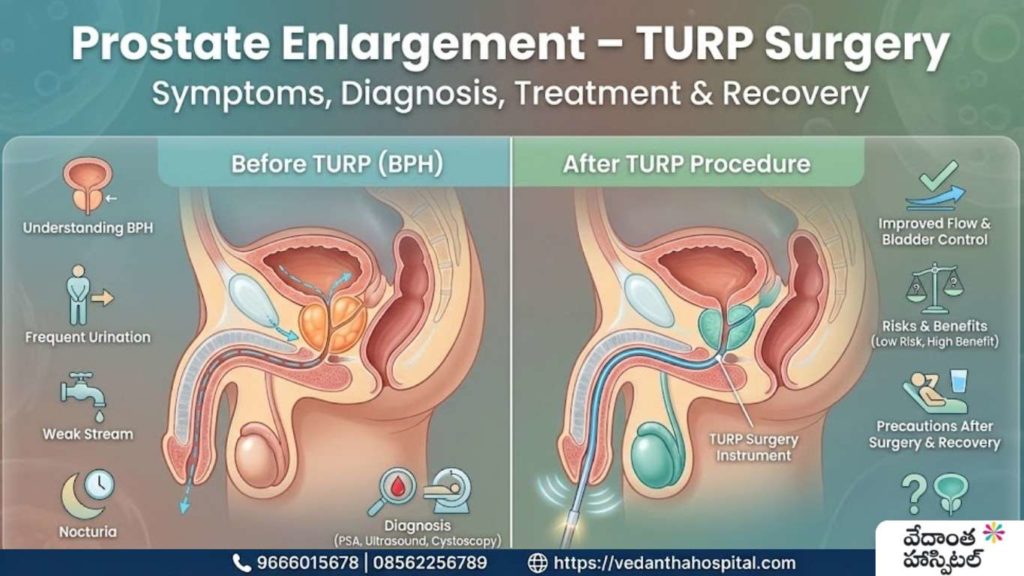
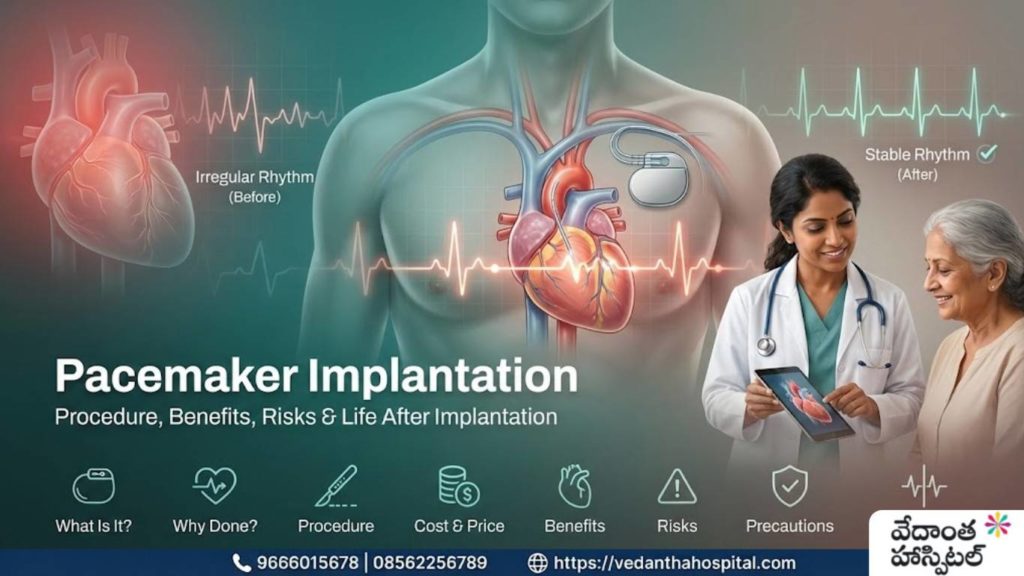
Pediatric Heart Surgeries – Congenital Defects
Congenital heart conditions are among the most common birth-related medical issues seen in children worldwide. Advances in pediatric cardiology and pediatric heart surgeries have significantly improved survival rates and long-term outcomes for children born with congenital defects. Understanding these conditions, their causes, diagnosis, and available treatments helps parents take informed decisions at the right time.
This blog provides a detailed, easy-to-understand overview of pediatric heart surgeries for congenital defects, including symptoms, types, diagnostic methods, treatment approaches, and long-term care.
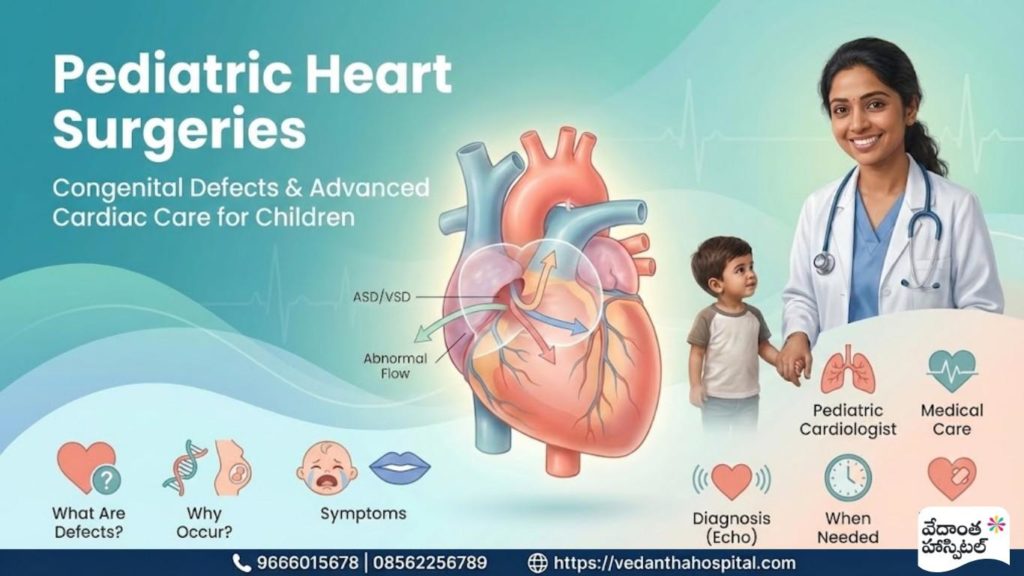
Pediatric Heart Surgeries
Pediatric heart surgeries are specialized surgical procedures performed to correct heart problems present at birth, also known as congenital heart defects. These defects occur when the heart or major blood vessels do not develop normally during pregnancy.
Congenital defects can range from mild conditions that resolve on their own to complex abnormalities requiring immediate surgical intervention. With early diagnosis and expert care, many children grow up to lead healthy, active lives.
Modern care at a Multispeciality Hospital in Kadapa allows early screening, diagnosis, and referral for timely treatment when required.
What Are
Congenital Heart Defects?
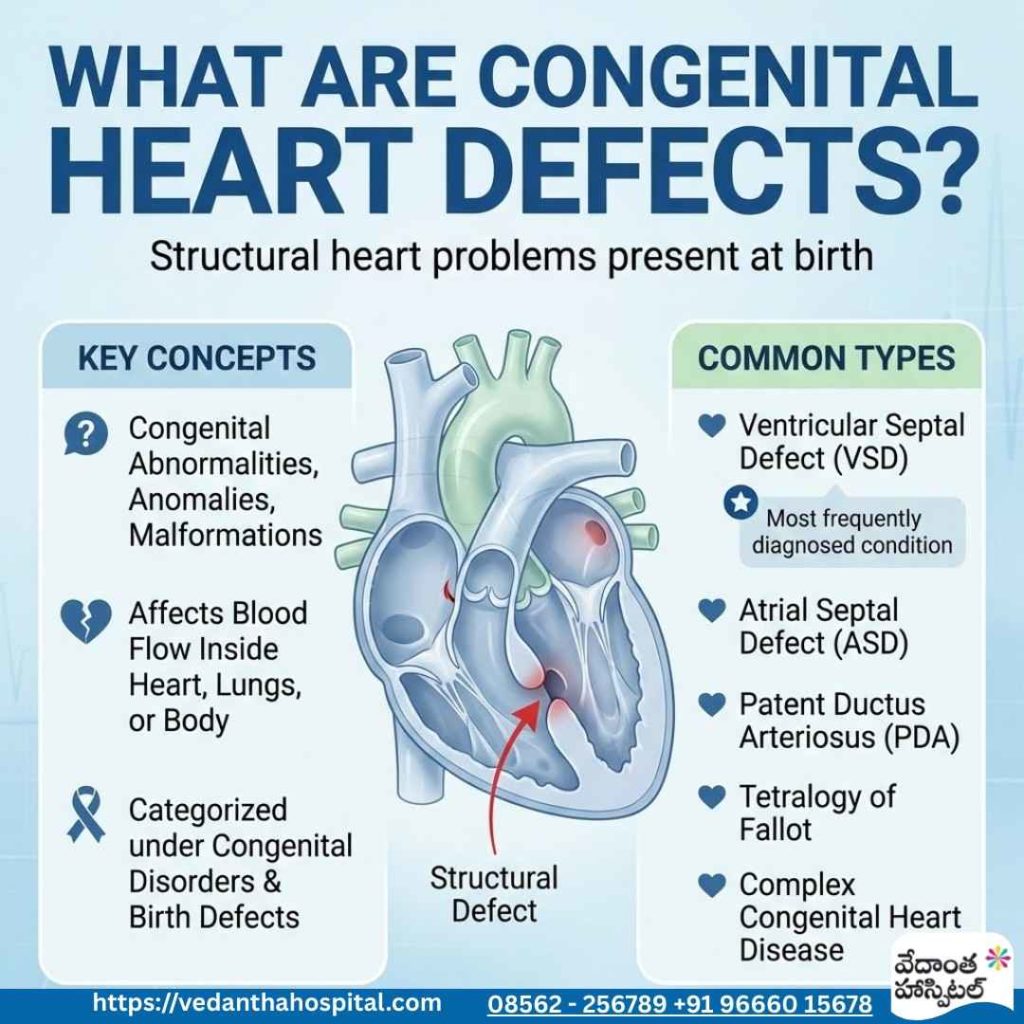
Congenital heart defects are structural problems of the heart present at birth. They are a subset of congenital abnormalities, congenital anomalies, and congenital malformations affecting the heart.
Some defects affect blood flow inside the heart, while others impact how blood flows to the lungs or the rest of the body. These conditions are also categorized under congenital disorders and birth defects.
Common Types of Congenital Heart Defects
- Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD)
- Atrial Septal Defect (ASD)
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)
- Tetralogy of Fallot
- Complex congenital heart disease
Among these, congenital heart disease VSD is one of the most frequently diagnosed conditions.
Why Do Congenital Heart Defects Occur?
The exact cause of many congenital defects is not always known. However, several risk factors are associated with their development:
- Genetic conditions and family history
- Birth defects during pregnancy
- Poor maternal nutrition
- Infections during pregnancy
- Diabetes or uncontrolled medical conditions in the mother
These conditions fall under birth defects causes and may affect overall fetal development, including the heart.
Symptoms and Early Signs
in Children
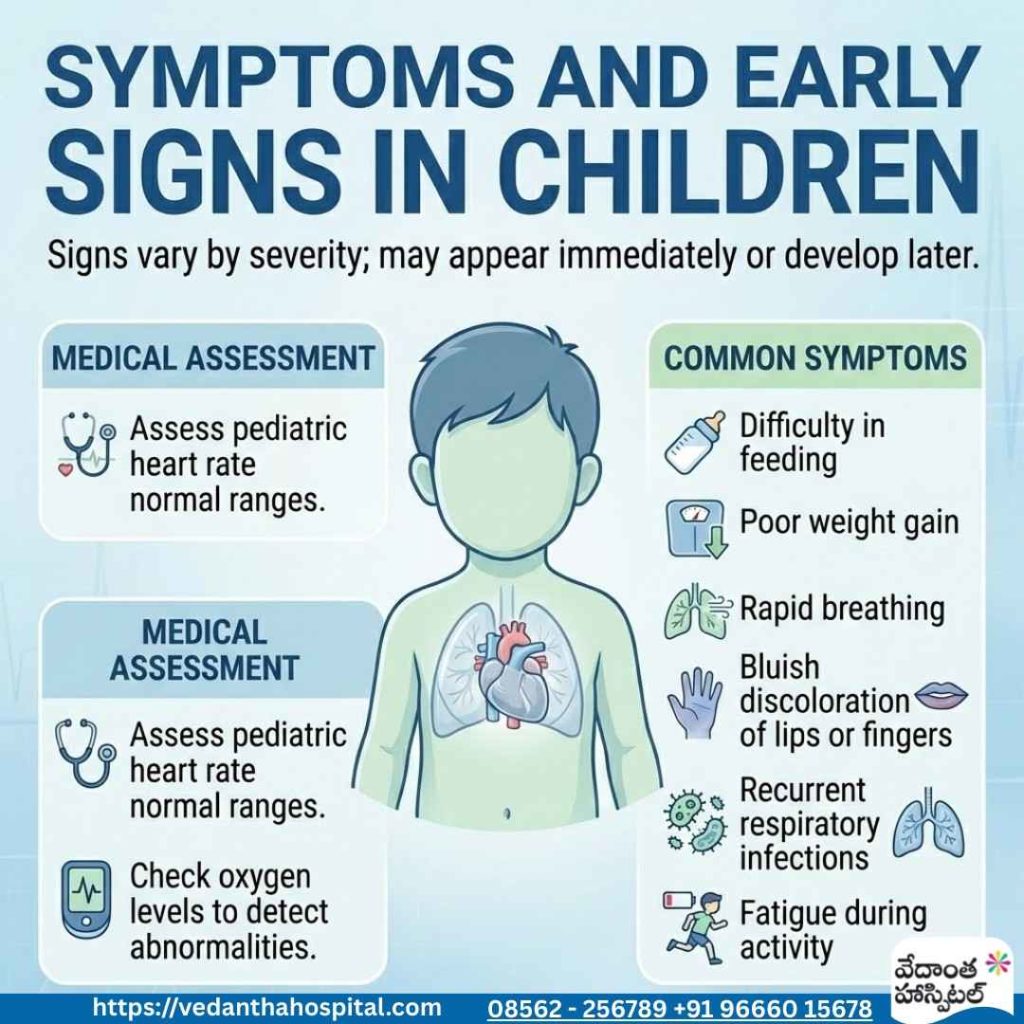
Symptoms vary depending on the severity and type of defect. Some babies show symptoms immediately, while others develop signs later in childhood.
Common Symptoms
- Difficulty in feeding
- Poor weight gain
- Rapid breathing
- Bluish discoloration of lips or fingers
- Recurrent respiratory infections
- Fatigue during activity
Doctors often assess pediatric heart rate normal ranges and oxygen levels to detect early abnormalities.
Diagnosis and Evaluation of Pediatric Heart Conditions
Early and accurate diagnosis plays a crucial role in managing congenital heart defects in children. Pediatric heart conditions are often detected through a combination of clinical examination and specialized diagnostic tests. These evaluations help doctors understand the type, severity, and impact of the defect, allowing timely treatment planning.
Diagnostic Method | Purpose | What It Helps Detect |
Clinical Examination | Initial assessment of the child’s overall health | Heart murmurs, abnormal breathing, cyanosis (bluish skin), delayed growth |
Echocardiography (2D Echo) | Primary imaging tool in pediatric cardiology | Structural defects such as holes in the heart (ASD, VSD), valve abnormalities, blood flow patterns |
Electrocardiogram (ECG) | Measures electrical activity of the heart | Abnormal heart rhythms, chamber enlargement, conduction issues |
Chest X-ray | Evaluates heart size and lung condition | Enlarged heart, fluid in lungs, abnormal blood circulation |
Pulse Oximetry | Measures oxygen levels in blood | Detects low oxygen saturation, especially in newborns |
Cardiac CT / MRI | Advanced imaging for complex cases | Detailed heart anatomy, complex congenital anomalies |
Cardiac Catheterization | Invasive diagnostic and sometimes therapeutic test | Measures pressures inside heart chambers and blood vessels |
Prenatal Fetal Echo | Screening during pregnancy | Early detection of congenital heart defects before birth |
These diagnostic methods are commonly used in pediatric cardiology to ensure accurate identification of congenital heart disease and guide treatment decisions. Early diagnosis significantly improves surgical outcomes and long-term heart function.
Pediatric Heart Surgery: When Is It Needed?
Not all congenital heart defects require surgery. However, pediatric heart surgery becomes necessary when:
- Blood flow is severely restricted
- Oxygen levels are dangerously low
- Heart failure symptoms develop
- The defect does not close naturally
Conditions such as pediatric heart failure often require surgical correction to prevent long-term complications.
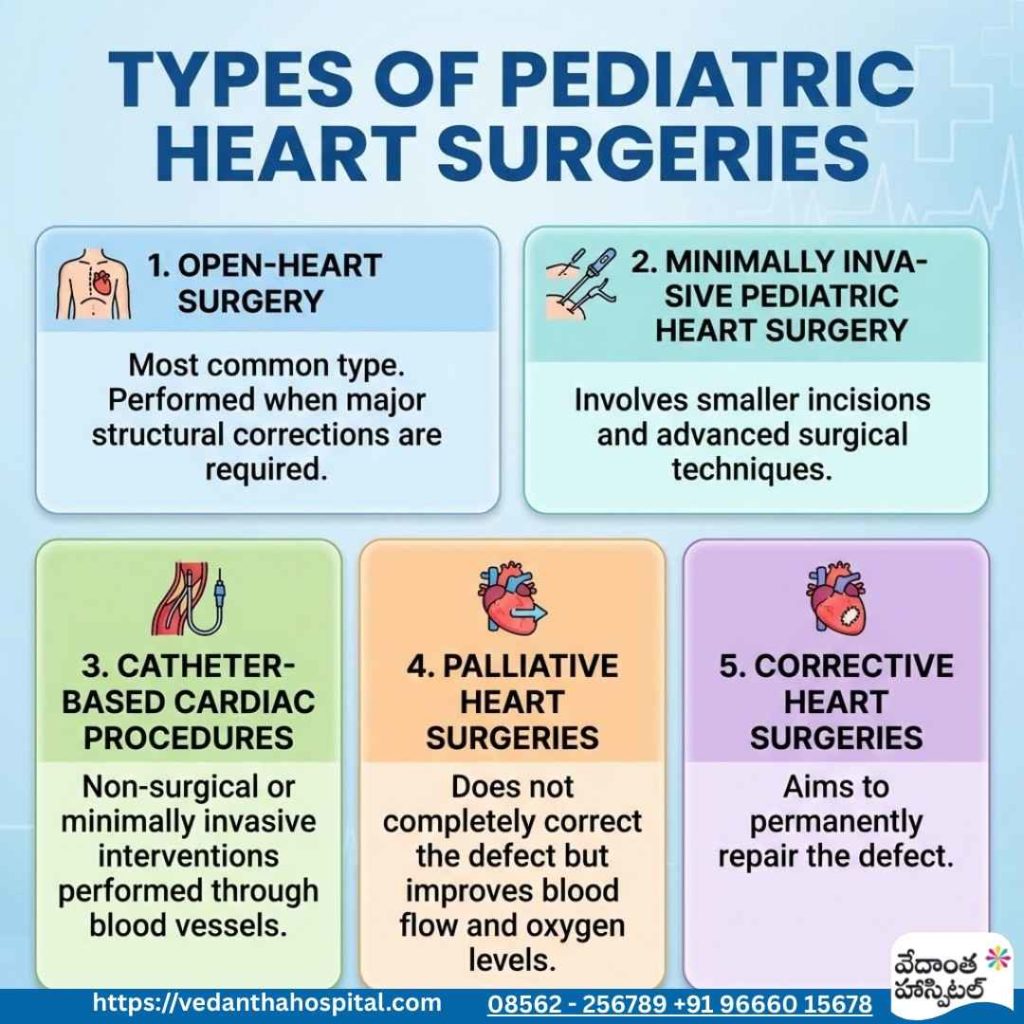
Types of Pediatric Heart Surgeries
1. Open-Heart Surgery
This is the most common type of pediatric heart surgery and is performed when major structural corrections are required.
2. Minimally Invasive Pediatric Heart Surgery
These procedures involve smaller incisions and advanced surgical techniques.
3. Catheter-Based Cardiac Procedures
These are non-surgical or minimally invasive interventions performed through blood vessels.
4. Palliative Heart Surgeries
These surgeries do not completely correct the defect but improve blood flow and oxygen levels.
5. Corrective Heart Surgeries
Corrective surgeries aim to permanently repair the defect.
6. Emergency Pediatric Heart Surgeries
In some cases, immediate surgery is required to save the child’s life.
Why Early Surgical Intervention Matters
Early detection and timely pediatric heart surgery:
- Prevents irreversible heart damage
- Supports normal physical and mental development
- Reduces long-term complications
- Improves survival and quality of life
With advancements in surgical techniques and post-operative care, outcomes for children with congenital heart defects have improved dramatically.
Post-Surgery Recovery and Long-Term Care
After surgery, children are monitored in specialized cardiac care units. Recovery depends on the complexity of the defect and the procedure performed.
Long-term care includes:
- Regular follow-up visits
- Monitoring growth and development
- Heart function assessments
- Lifestyle guidance for parents
Many children go on to live normal lives with proper medical supervision.
Role of Pediatric Cardiology
- Pediatric cardiology focuses on diagnosing and managing heart conditions in infants and children. Specialists evaluate heart structure, rhythm, and function at different stages of growth.
- Care teams often work closely with families to explain conditions, treatment options, and expected outcomes in simple terms.
Importance of Multidisciplinary Care
Comprehensive pediatric heart care involves collaboration between:
- Pediatric cardiologists
- Cardiac surgeons
- Cardiac anesthesiologists
- Intensive care specialists
Facilities at a Multispeciality Hospital in Kadapa allow coordinated care under one roof, improving outcomes for complex congenital heart conditions.
Pediatric Heart Care in Kadapa
- Access to advanced pediatric heart services locally helps families seek timely care. Facilities such as a Cardiology Hospital in Kadapa and a Cardiothoracic Surgery Hospital in Kadapa play an essential role in managing congenital heart diseases.
- At Vedanta Hospitals in Kadapa, pediatric heart conditions are managed through structured evaluation, treatment planning, and follow-up care. Expert supervision by specialists, including Dr. Ashok Kumar, supports safe surgical and post-operative management.
Conclusion
- Pediatric heart surgeries play a vital role in correcting congenital defects and improving the quality of life for affected children. Early diagnosis, expert care, and structured follow-up are key to successful outcomes. With advancements in pediatric cardiology and surgical techniques, children with congenital heart conditions have better chances than ever before to grow and thrive.
- For location details, patient feedback, and service updates related to pediatric and cardiac care, parents may refer to the Google Business Profile (GMB) of Vedanta Hospitals. This helps access verified local information and directions easily.
FAQ'S
1. What are congenital heart defects?
Congenital heart defects are structural problems of the heart present at birth that affect blood flow or heart function.
2. Are congenital heart defects common in children?
Yes, they are among the most common birth defects worldwide and vary from mild to severe.
3. Can congenital heart defects be cured?
Many congenital heart defects can be corrected or managed effectively with surgery or medical care.
4. What is the most common congenital heart defect?
Ventricular septal defect (VSD) is one of the most common congenital heart conditions.
5. When is pediatric heart surgery required?
Surgery is needed when the defect affects oxygen supply, blood flow, or leads to heart failure symptoms.
6. Is pediatric heart surgery safe?
With modern techniques and expert care, pediatric heart surgeries have high success rates.
7. How long is recovery after pediatric heart surgery?
Recovery varies by procedure, but many children recover within weeks under proper care.
8. Can children live normally after heart surgery?
Yes, many children lead healthy and active lives with regular follow-up.
9. How are congenital heart defects diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves clinical examination, imaging tests, and cardiac evaluations.
10. Should parents worry about long-term complications?
With early treatment and follow-up, most long-term risks are well controlled.